SystemV共享内存
Nevermore 2022-12-01 OS
# SystemV 共享内存
- 进程间通信(interprocess communication——IPC)允许两个独立的进程进行数据交换,即相互发送数据和接收数据。进程间通信有两种基本模型:共享内存和消息传递。在共享内存模型中,建立了一个由协作进程共享的内存区域,然后,进程可以通过向共享区域读写数据来交换信息。在消息传递模型中,通信通过协作进程之间交换的消息进行。共享内存可能比消息传递更快,因为消息传递通常需要系统调用来实现,因此需要更耗时的内核干预任务。消息传递对于交换少量数据很有用,因为不需要避免冲突。在共享内存系统中,仅在建立共享内存区域时才需要系统调用。一旦建立了共享内存,所有访问都被视为例行内存访问,不需要内核的帮助。
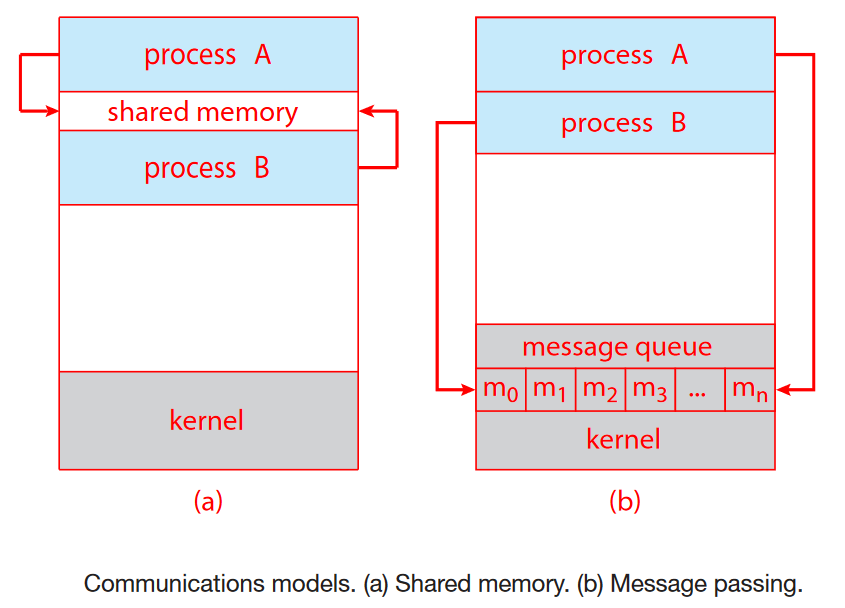
通过系统调用,将多个进程地址空间的部分区域映射到同一份物理内存,从而形成共享内存。共享内存具有最大的通信速度和便利性,因为它可以在计算机中以内存传输速度完成通信。然而,共享内存在多进程访问的同步和互斥方面存在问题,需程序员自行保证数据安全。
进程运行结束,系统创建的IPC资源并不会释放,它的生命周期由内核决定。可以通过以下命令查看并手动释放:
[test@VM-12-4-centos SystemVIPC]$ ipcs -m ------ Shared Memory Segments -------- key shmid owner perms bytes nattch status # perms代表文件权限 0x66010da7 0 test 664 4096 0 [test@VM-12-4-centos SystemVIPC]$ ipcrm -m 0 #shmid [test@VM-12-4-centos SystemVIPC]$ ipcs -m ------ Shared Memory Segments -------- key shmid owner perms bytes nattch status1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11SystemV 共享内存的系统调用:
- 分配共享内存
#include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/shm.h> int shmget(key_t key, size_t size, int shmflg);1
2
3key:必须是IPC独立私有的值。可以通过
ftok()生成#include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/ipc.h> key_t ftok(const char *pathname, int proj_id);1
2
3失败返回-1;成功返回System V IPC key。当pathname和proj_id相同时,生成的key是相同的。
size:系统给共享内存分配的大小实际是
PAGE_SIZE(4Kb)的整数倍。shmflg:
IPC_CREAT:存在则获取,不存在则创建一块新的内存区域;IPC_EXCL:与创建选项一起使用,若已经存在则创建失败,保证创建的共享内存是第一次创建的。返回值:成功创建返回共享内存的ID;失败则返回-1。
- 删除共享内存
#include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/shm.h> int shmctl(int shmid, int cmd, struct shmid_ds *buf);1
2
3cmd:
IPC_RMID:删除共享内存buf:shmid的data struct,用来描述共享内存的属性
- 将共享内存与进程的虚拟地址空间进行挂接
#include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/shm.h> void *shmat(int shmid, const void *shmaddr, int shmflg);1
2
3shmid:
shmget()的返回值,为共享内存的ID(类似于数组下标)shmaddr:虚拟地址空间的地址,设置为NULL会由操作系统进行分配。
shmflg:设0由操作系统管理。
返回值:成功返回共享内存的段地址——虚拟地址。
- 将共享内存与当前进程解挂接
int shmdt(const void *shmaddr);1shmaddr:
shmat()的返回值。
下面是一段例程说明SystemV共享内存的使用:
- SharedPath.h
#pragma once
#define PipeFilePath "PipeFile"
#define IPC_ID 0x1666
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
- server.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "SharedPath.h"
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int main()
{
key_t KeyVal = ftok(PipeFilePath, IPC_ID);
if(KeyVal == -1)
{
perror("ftok failed\n");
exit(-1);
}
//int id = shmget(KeyVal, 4096, IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0664);
int id = shmget(KeyVal, 4096, IPC_CREAT | 0664); //在物理内存中开辟了一段共享空间
if(id < 0)
{
perror("shmget failed\n");
exit(-2);
}
char* Virtualaddr = (char*)shmat(id, NULL, 0);
// ************共享内存使用****************
while(1)
{
printf("%s\n", Virtualaddr); //读取,不会等待其他线程写入
fflush(stdout);
sleep(1);
if(Virtualaddr == NULL)
{
break;
}
}
//***************************************
shmdt(Virtualaddr);
shmctl(id, IPC_RMID, NULL); //释放共享内存空间
return 0;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
- client.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "SharedPath.h"
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int main()
{
key_t KeyVal = ftok(PipeFilePath, IPC_ID);
if(KeyVal == -1)
{
perror("ftok failed\n");
exit(-1);
}
int id = shmget(KeyVal, 4096, IPC_CREAT); //获取已存在的IPC ID。
if(id < 0)
{
perror("shmget failed\n");
exit(-2);
}
char* Virtualaddr = (char*)shmat(id, NULL, 0);
// ************共享内存使用****************
int i = 0;
while(1)
{
for(i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Virtualaddr[i] = 'a';
sleep(5);
}
Virtualaddr[i] = '\n';
Virtualaddr[i + 1] = '\0';
}
//***************************************
shmdt(Virtualaddr);
return 0;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
- Makefile
.PHONY:all
all:client server
client:client.c
gcc -o $@ $^
server:server.c
gcc -o $@ $^
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f client server
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
